Explore Pharmaceutical Formulation Companies in India – Medicef Pharma Insights
Explore leading pharmaceutical formulation companies in India through Medicef Pharma Insights. Stay informed and elevate your understanding of the market.
Antibiotics are a cornerstone in the fight against bacterial infections around the world. They save countless lives every year and have changed medicine forever. Among these, beta lactam antibiotics are some of the most used and studied drugs in medical history. But as bacteria grow smarter and resistant to treatments, understanding how these drugs work becomes even more important.
Beta lactam antibiotics are drugs that attack bacteria by targeting their cell walls. They all share a common chemical structure called the beta lactam ring. This makes them part of a larger family with several subclasses. The main groups include:
The story begins in the 1920s with the discovery of penicillin. Its success led to the development of other beta lactam drugs over the years. Important milestones include the creation of broad-spectrum antibiotics in the '60s and the rise of carbapenems in the '80s. These advances made it possible to treat more types of bacterial infections effectively.
Beta lactam antibiotics are a go-to choice in hospitals and clinics for many infections. They are used to treat pneumonia, urinary tract infections, skin infections, and even meningitis. Their ability to kill bacteria quickly and safely makes them essential for saving lives and reducing illness.
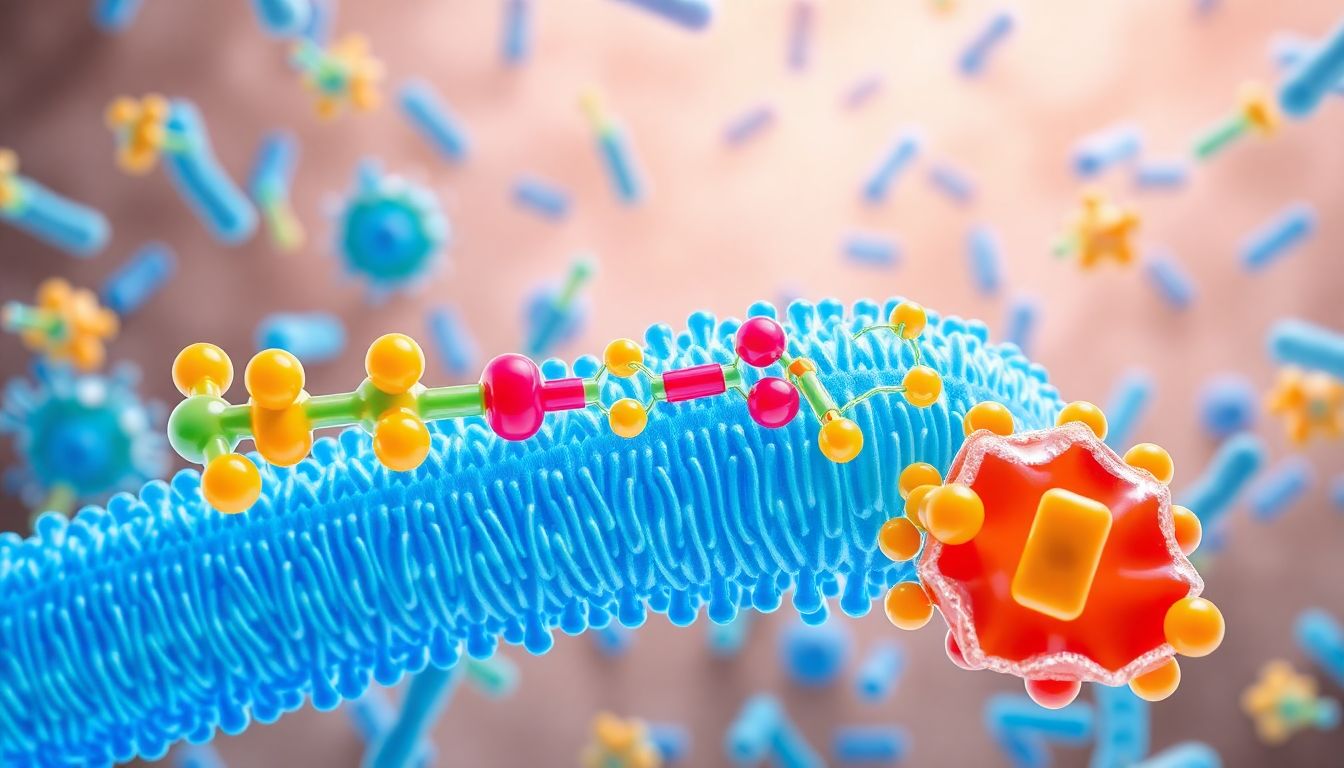
Bacteria have a tough outer layer called the cell wall made of peptidoglycan. This wall keeps bacteria stable and protects them from external harm. To survive, bacteria must constantly build and repair this wall. Beta lactam antibiotics specifically target this process, stopping bacteria from growing stronger.
Inside bacteria are special enzymes called penicillin-binding proteins, or PBPs. These are like tiny construction workers that link pieces of peptidoglycan together. Beta lactam antibiotics attach to these PBPs, blocking their work. Without these enzymes functioning, the cell wall becomes weak and unstable.
As the cell wall breaks down, bacteria can't hold their shape. They become vulnerable to the environment. Water rushes in, causing the bacteria to burst open—a process called lysis. This kills the bacteria quickly, making beta lactam antibiotics bactericidal, or bacterial killers.
Some bacteria produce enzymes called beta lactamases. These enzymes cut open the beta lactam ring of the antibiotic, rendering it useless. This is the most common way bacteria resist beta lactam drugs and leads to treatment failures.
Bacteria can mutate their PBPs to reduce drug binding. A famous example is MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), which has PBPs that don’t let beta lactams stick. This makes infections harder to treat.
Bacteria can change their cell wall to prevent antibiotics from entering. They also develop pump systems called efflux pumps that push antibiotics out of the cell. Both strategies lower the amount of drug inside bacteria, decreasing effectiveness.
To fight resistance, doctors sometimes add beta lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid with penicillins. These inhibitors block beta lactamases, protecting the antibiotic. Research also focuses on creating new beta lactams that bacteria can't easily resist.
Beta lactam antibiotics are used to treat a wide range of infections:
The right dose depends on the infection and patient. Doctors consider factors like age, weight, and kidney function. Timing and frequency are also crucial to maintain enough drug in the body to kill bacteria.
Most people tolerate beta lactams well. Allergic reactions can occur, ranging from rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Some experience gastrointestinal issues like nausea or diarrhea. Careful monitoring helps prevent complications.
Scientists are working on developing new versions of beta lactams that bypass resistance. Combining drugs with beta lactamase inhibitors is one strategy. Another involves designing molecules that can stick to even resistant bacteria, keeping us a step ahead.
Beta lactam antibiotics play a vital role in fighting bacterial infections and saving lives. Knowing how they work helps us understand their power and limits. As bacteria become more resistant, using these drugs wisely and developing new medicines are crucial steps forward. Healthcare providers and patients must work together to prevent resistance, ensuring these antibiotics remain effective for generations to come. Remember, prudent use and proper treatment are key to staying ahead in the ongoing battle against bacterial infections.
Explore leading pharmaceutical formulation companies in India through Medicef Pharma Insights. Stay informed and elevate your understanding of the market.
Explore the synergy of CO-AMOXICLAV and Lactic Acid Bacillus. Uncover their roles in promoting health and fighting infections effectively.
Discover how beta-lactam antibiotics combat bacterial infections by disrupting cell wall synthesis. Learn about their mechanisms and effectiveness today.
Explore our premium ready-to-compress granules designed for tablet formulation. Achieve optimal results in your production with our innovative materials.
Discover how we ensure quality pharmaceuticals remain affordable, making healthcare accessible for all. Explore our commitment to excellence and value.
Discover the comprehensive guide to Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid Sachet BP. Learn about its uses, benefits, and important dosage information for effective treatment.